Select image to enlarge
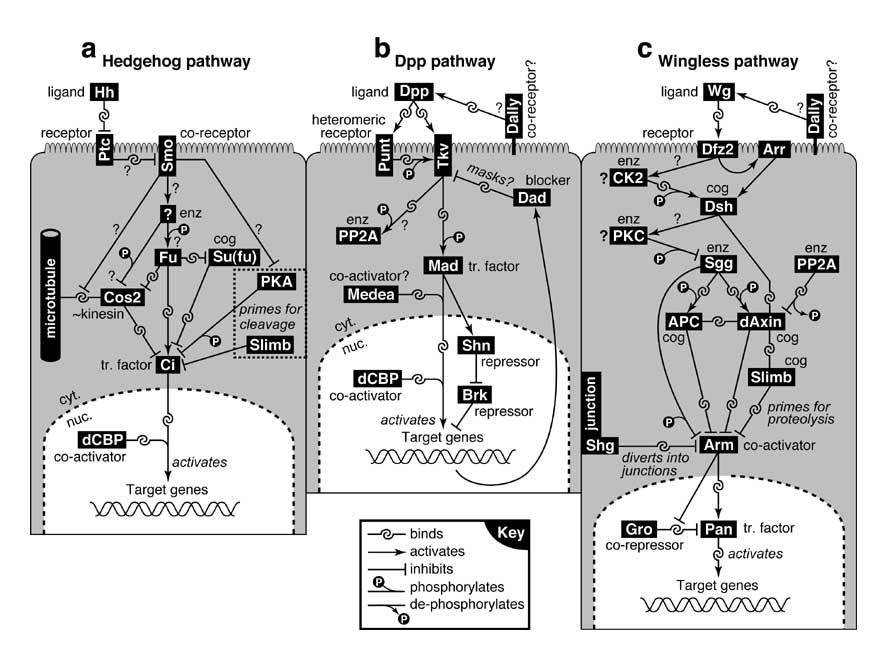
Figure 5.6
Some key signaling pathways in disc development.
In the working models depicted here, certain components may be replaced by others (not shown) in different tissues, regions, or time periods. Three cells are depicted, with apical microvilli at top, though receptor-ligand interactions may actually take place elsewhere on the surface. Black rectangles = proteins; gray area = cytoplasm (cyt); dashed line = nuclear membrane. Arrows (activation) and blunt —| lines (repression) indicate epistatic relations. Noncovalent binding is symbolized by interlocking hooks (cf. key). Question marks concern how or whether the interactions occur (see text). A 'cog' (a.k.a. 'adaptor') is a component that plays a steric (non-enzymatic) role [441, 1954, 3299, 3676] (e.g., Slimb [2668]). Enz = enzyme, CK2 = Casein kinase 2, PKA = Protein kinase A (likewise PKC), Shg = Shotgun (a.k.a. dE-cadherin). For other abbreviations see App. 6. For perspective see App. 7.
a. Hedgehog pathway [1554, 1974, 2075, 3685, 3831]. Binding partners (listed from surface to DNA) are based on fly studies or vertebrate homologs (VH): Hh-Ptc [755]Δ, Ptc-Smo (VH [4130]), Fu-Cos2 [4068]Δ, Fu-Ci [4068], Fu-Su(fu) [4068]Δ, Cos2-microtubules [3612, 3976], Cos2-Ci [4068, 4536]Δ, Su(fu)-Ci [4068]Δ, dCBP-Ci [54], Ci-DNA [751]Δ. Ci's interaction with dCBP may be inhibited by PKA (link not shown) [54].
b. Dpp pathway [959, 1983, 3498]. Dally is placed upstream of Dpp based on the ability of extra doses of dpp+ to suppress dallyLOF phenotypes [2004], and a similar argument applies to Wg [2556]Δ. Evidence for binding: Dpp-Punt [2495], Dpp-Tkv [2495]Δ, Dpp-proteoglycans (e.g., Dally) [2004]Δ, Punt-Tkv [2495], Tkv-Mad [1983], Tkv-Dad [1983], Tkv-PP2A (VH [1627]), Mad-Medea [1983, 4703], Mad-dCBP [4534], Mad-DNA [2217]. Mad may also bind microtubules (not shown) [1084]. The 'Shn —| brk' link does not actually occur at the protein level, but rather occurs via inhibition of brk transcription [2727].
c. Wingless pathway [422, 3919]. Arr is thought to be a co-receptor for Dfz2, but it does not present Wg in the same way as Dally [4570]. Conceivably (not shown) Arr may act via CK2: Dfz2 —> Arr —> CK2 —> Dsh, etc. The APC homolog here (labeled simply APC) is likely E-APC [4832]. Sgg is thought to be Arm's natural kinase [3683] (but see [3228, 4062]). Evidence for binding (see [3316] for details): Wg-Dfz2 [310], Wg-proteoglycans like Dally [598]Δ, CK2-Dsh [3149, 4676], Dsh-dAxin (VH [2238]Δ), Sgg-APC (VH [3675]), Sgg-dAxin [3683], APC-dAxin [1698], PP2A-dAxin (VH [1919]), dAxin-Slimb (VH [2241]), APC-Arm [4832], dAxin-Arm [1698], APC-Arm [4832], Slimb-Arm (VH [4701]Δ), Shg-Arm [3749, 4268, 4416]Δ, Arm-Pan [519, 4439], Gro-Pan [692, 2496], Pan-DNA [519, 4439].
|
|
